Tin:
the main characterof technological evolution
Tin is a metal, which physical and chemical properties have fostered technological innovations throughout history.
Since it was combined with copper, at the beginning of the Bronze Age -more than 5,000 years ago-, tin has adapted to the changing needs of each technological era due to its versatility. After several centuries, tin still plays a crucial role in societal transformation, now oriented towards a more sustainable direction.
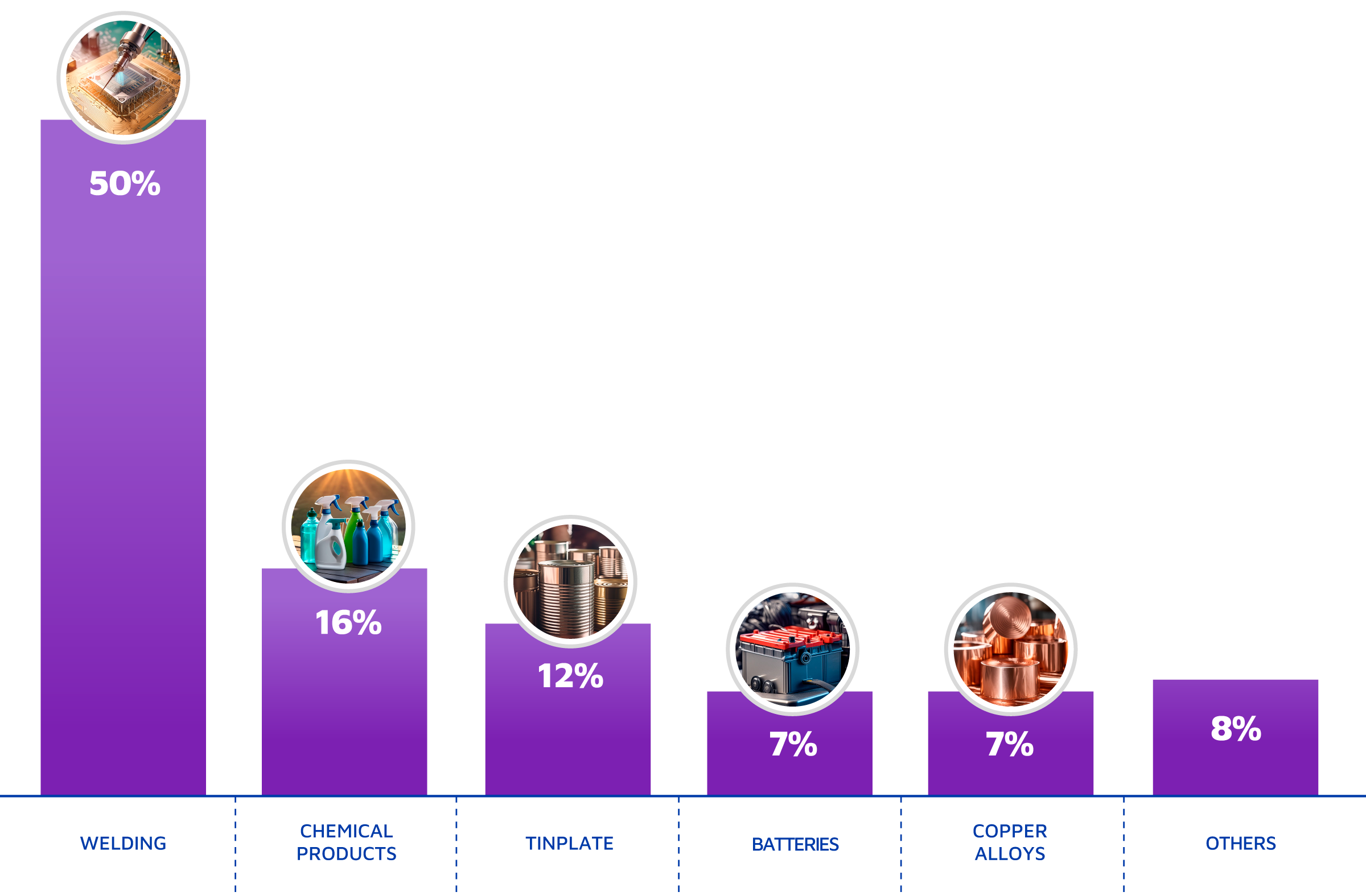
It was used to coat steel to produce tinplate, due to its malleability and corrosion resistance. This metal has played a fundamental role since the XVIII century, radically transforming the preservation and distribution of perishable products, such as food.
Furthermore, due to tin being able to conduct electricity and its low melting point, it is the ideal material for welding and electronic circuit connection. Thus, this mineral has been an essential part in the development of information and communication technologies in the digital era, from the first radios to the newest smartphones.
Tin is also a key element for the efficiency of sustainable energy generation and storage technologies, such as solar panels and electric cars’ batteries.
These are only a few examples of tin uses. It is a versatile metal that stands the test of time and its history is a testimony of human capacity to create, connect, and innovate.